

“And it is at its worst between 3 and 4 in the morning.” Even in healthy people, “your best lung function is between noon and 4 p.m.,” said Ileen Gilbert, MD, a pulmonary specialist at Froedtert & The Medical College of Wisconsin. It’s not unusual for asthma symptoms to worsen after dark. So, what is nocturnal asthma? Also called nighttime asthma, it is the type of asthma that gets worse at night. Sputum characteristics and airway clearance methods in patients with severe COVID-19.If you wake up at night coughing, wheezing, and feeling breathless, you could have nocturnal asthma. United States: Jones & Bartlett Learning.
Respiratory care: patient assessment and care plan.
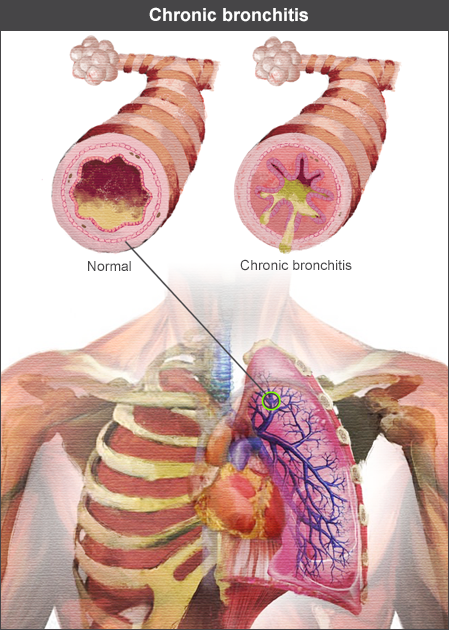
#Nocturnal asthma left lung mucous trial#
A pilot, open labelled, randomised controlled trial of hypertonic saline nasal irrigation and gargling for the common cold.
Marvels of mucus and phlegm: The slime that keeps you healthy. Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy. We link primary sources - including studies, scientific references, and statistics - within each article and also list them in the resources section at the bottom of our articles. Medical News Today has strict sourcing guidelines and draws only from peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical journals and associations. surgery, such as a left ventricular assist device, coronary artery bypass grafting, or angioplasty. implantable devices, such as a defibrillator. medication therapy, such as an angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor, loop diuretic, or beta-blocker. lifestyle changes, such as exercising regularly and eating a balanced, nutritious diet. Heart failure is a serious condition that requires immediate medical treatment. In most cases of asthma, people can effectively manage their symptoms with medication, such as quick-relief and corticosteroid inhalers. Lung diseaseĪ doctor might recommend the following treatments for COPD: It is important that a person finishes the entire course of antibiotics, even if their cough and phlegm go away sooner. Infections that affect the lower respiratory tract may require treatment from a doctor, who will most likely prescribe an antibiotic. Over-the-counter decongestants and other products can help with some symptoms in the meantime. Most upper respiratory infections will go away on their own. The primary treatment for allergies is to identify and avoid triggers. medications, which might include antacids to help relieve heartburn. lifestyle changes, such as stopping smoking and avoiding foods that trigger heartburn. Management strategies for GERD and LPR include: The treatment for coughing up phlegm depends on its cause. It is vital to report these symptoms to a doctor for immediate treatment. swelling of the ankles, legs, feet, and abdomen. Heart failure is a condition in which the heart cannot correctly pump or relax to circulate blood around the body. Some lung diseases, such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), cause a persistent cough and excess phlegm. Learn more about air pollution and its effects on health here. This irritation can cause a cough with excess phlegm. Environmental factorsĮxposure to certain irritants, such as smoke and other fumes, can irritate the airway. This can cause a person to cough up phlegm. Some people with allergies may also develop a postnasal drip, which occurs due to excess mucus production that leaks down the throat. This can cause heartburn and other symptoms, including:Īllergic rhinitis causes similar symptoms to a cold, such as: LPR can occur due to dysfunction in the lower esophageal sphincter, esophagus, and upper esophageal sphincter. However, in people with LPR, stomach acid can move up into the esophagus, the voice box, and even the nasal cavity. Laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR) is similar to GERD. The main symptom of GERD is heartburn, though acid reflux can also cause a cough.Īpproximately 18–28% of people in the United States will experience GERD at some point. GERD can occur due to dysfunction in the lower esophageal sphincter, a hiatal hernia, or dysfunction in the esophagus. Other possible causes of coughing up phlegm include: Acid refluxĪcid reflux, also known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), is when stomach acid moves up into the esophagus (food pipe). They may produce longer-lasting symptoms. Lower respiratory tract infections, which include bronchitis and pneumonia, are more serious. These illnesses will typically also cause: Share on Pinterest Illustration by Jason Hoffman.Ĭough and excess mucus production are common symptoms of upper respiratory tract infections.






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
