
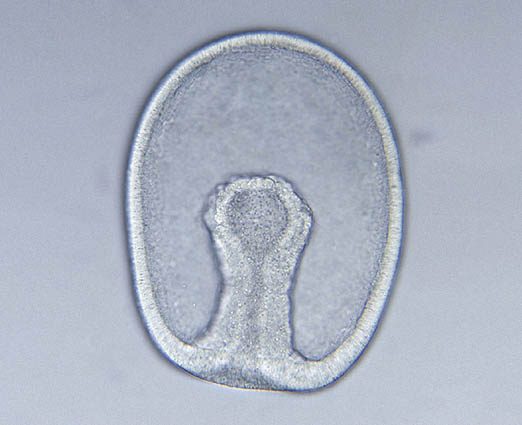
The Biomarker Guide: Biomarkers and isotopes in petroleum systems and Earth history. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. "Assessing the root of bilaterian animals with scalable phylogenomic methods". "The developmental basis for the recurrent evolution of deuterostomy and protostomy". Animal Evolution - Genomes, Fossils, and Trees. "The mouth, the anus, and the blastopore - open questions about questionable openings". Urbilaterian, a hypothethical common ancestor to Protostomes and Deuterostomes.Embryological origins of the mouth and anus.The timing of clades radiating into newer clades is given in mya (millions of years ago) less certain placements are indicated with dashed lines. A modern consensus phylogenetic tree for the protostomes is shown below. molluscs, annelids, platyhelminths, and rotifers). arthropods, nematodes) and the Spiralia (e.g. Protostomes are divided into the Ecdysozoa (e.g. Protostomes evolved into over a million species alive today, compared to about 60,000 deuterostome species. The two clades diverged about 600 million years ago. The common ancestor of protostomes and deuterostomes was evidently a worm-like aquatic animal of the Ediacaran. Spiral cleavage happens because the cells' division planes are angled to the polar major axis, instead of being parallel or perpendicular to it.Īnother difference is that secondary body cavities ( coeloms) generally form by schizocoely, where the coelom forms out of a solid mass of embryonic tissue splitting away from the rest, instead of by enterocoelic pouching, where the coelom would otherwise form out of in-folded gut walls. Many protostomes (the Spiralia clade) undergo spiral cleavage during cell division instead of radial cleavage. Protostome and deuterostome embryos differ in several other ways. It is now known that the fate of the blastopore among protostomes is extremely variable while the evolutionary distinction between deuterostomes and protostomes remains valid, the descriptive accuracy of the name protostome is disputable. The protostomes (from Greek πρωτο- prōto- 'first' + στόμα stóma 'mouth') were so named because it was once believed that in all cases the embryological dent formed the mouth while the anus was formed later, at the opening made by the other end of the gut. 'second-mouth'), the original dent becomes the anus while the gut eventually tunnels through to make another opening, which forms the mouth. In the sister-clade, the deuterostomes ( lit. In animals at least as complex as earthworms, the first phase in gut development involves the embryo forming a dent on one side (the blastopore) which deepens to become its digestive tube (the archenteron). See also: embryological origins of the mouth and anus Together with the Deuterostomia and Xenacoelomorpha, these form the clade Bilateria, animals with bilateral symmetry, anteroposterior axis and three germ layers. They are also called schizocoelomates since schizocoely typically occurs in them.


Well known examples of protostomes are arthropods, molluscs, annelids, flatworms and nematodes. This nature has since been discovered to be extremely variable among Protostomia's members, although the reverse is typically true of its sister clade, Deuterostomia. ə/) is the clade of animals once thought to be characterized by the formation of the organism's mouth before its anus during embryonic development. Protostomia ( / ˌ p r oʊ t ə ˈ s t oʊ m i. Some protostomes representing the 6 phyla: Mantis religiosa ( Arthropoda), Caenorhabditis elegans ( Nematoda), Cornu aspersum ( Mollusca), Pseudoceros liparus ( Platyhelminthes), Lumbricus terrestris ( Annelida), Habrotrocha rosa ( Rotifera).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
